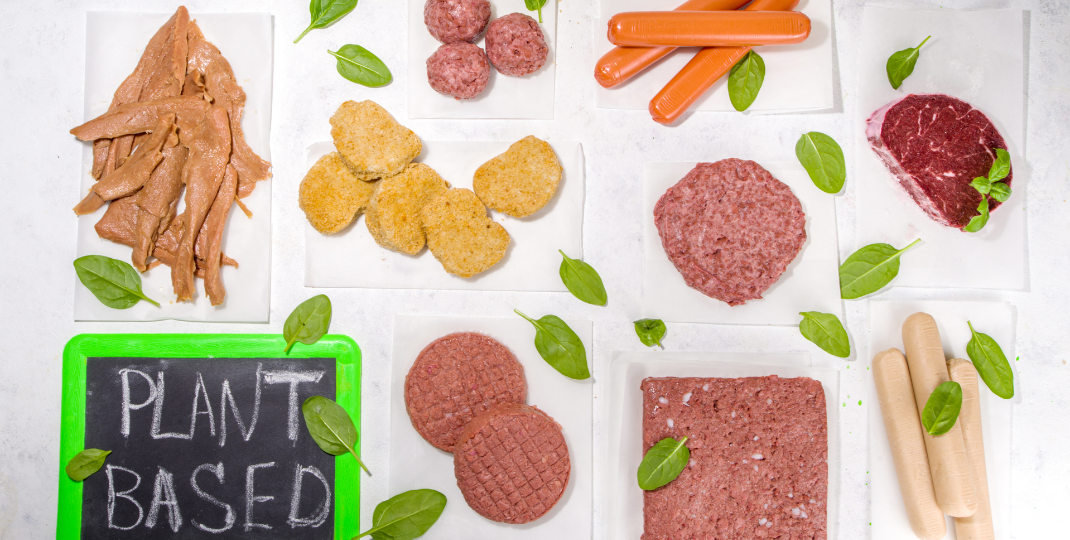
Vegan mycoprotein, also known as fungal protein or fungi-based protein, is a plant-based alternative to traditional animal-derived proteins. It is derived from fungi, such as mushrooms or filamentous fungi like Fusarium venenatum. Vegan mycoprotein offers a sustainable and ethical option for individuals following a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle, as it provides a rich source of essential amino acids without the need for animal products. This innovative protein source has gained popularity in recent years due to its numerous health benefits, including low fat content, high fiber content, and its ability to support muscle growth and repair. Furthermore, vegan mycoprotein is environmentally friendly, requiring less land, water, and resources compared to traditional livestock farming. With its versatility and nutritional profile, vegan mycoprotein is revolutionizing the plant-based protein market and providing an exciting new option for conscious consumers.

What is vegan mycoprotein made from?
How is vegan mycoprotein produced?
Vegan mycoprotein, such as the popular brand Quorn, is typically produced through a fermentation process using a fungus called Fusarium venenatum. The fungus is grown in large fermentation tanks containing a nutrient-rich medium, which allows it to multiply and produce mycelium. This mycelium is then harvested, filtered to remove any unwanted components, and processed into various forms like chunks or mince. The resulting mycoprotein is a complete protein source that can be used as a meat substitute in vegan and vegetarian diets.
Is vegan mycoprotein nutritionally equivalent to animal-based proteins?
Vegan mycoprotein is generally considered to be nutritionally equivalent to animal-based proteins. Mycoprotein, derived from fungi such as mushrooms and yeast, is a complete protein that contains all the essential amino acids required by the human body. It is also low in fat and cholesterol-free, making it a healthier alternative to animal-based proteins. Additionally, mycoprotein can be fortified with vitamins and minerals to enhance its nutritional profile. However, it is important to note that individual nutritional needs may vary, and a well-balanced and varied diet is key to meeting one's nutritional requirements.
Are there any potential health risks or side effects associated with consuming vegan mycoprotein?
There are generally no potential health risks or side effects associated with consuming vegan mycoprotein. It is a safe and nutritious alternative to animal-based proteins, with high levels of essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals. However, individuals with specific allergies or sensitivities to fungi might experience adverse reactions and should exercise caution. Additionally, like any food, the overall diet should be balanced and varied to ensure adequate intake of all necessary nutrients.
How does the taste of vegan mycoprotein compare to traditional animal-based proteins?

The taste of vegan mycoprotein can vary depending on the specific product and how it is prepared, but generally, it has a neutral or mild flavor. It does not have the same distinct taste as traditional animal-based proteins like beef or chicken. Some people find that mycoprotein has a slightly earthy or nutty taste, but this can be easily masked or enhanced with seasonings and spices. Overall, the taste of vegan mycoprotein is often described as versatile and adaptable, making it suitable for a wide range of culinary applications.

Can vegan mycoprotein be used as a complete protein source in a vegan diet?
Yes, vegan mycoprotein can be used as a complete protein source in a vegan diet. Mycoprotein is a high-quality protein derived from fungi and has all the essential amino acids necessary for the body's needs. It is a suitable alternative to animal-based proteins and can provide the recommended daily intake of protein for vegans. Additionally, mycoprotein is low in fat and cholesterol-free, making it a healthy choice for individuals following a plant-based diet.
Are there any specific cooking or preparation methods required for vegan mycoprotein?
What are the environmental impacts of producing vegan mycoprotein compared to traditional animal-based proteins?

Producing vegan mycoprotein has several environmental benefits compared to traditional animal-based proteins. Firstly, mycoprotein production generally requires less land, water, and energy resources. It has a smaller carbon footprint due to reduced greenhouse gas emissions from livestock. Additionally, mycoprotein production generates significantly lower levels of water pollution and deforestation, as it does not rely on intensive agriculture or the feed production associated with animal farming. Moreover, the use of mycoprotein reduces the pressure on fisheries, preserving marine ecosystems and helping maintain biodiversity. Overall, producing vegan mycoprotein presents a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly alternative to traditional animal-based proteins.
The Rise of Vegan Mycoprotein: A Game-Changer in Plant-Based Nutrition
In conclusion, vegan mycoprotein presents a promising and sustainable solution for addressing the growing demand for plant-based protein sources. Its numerous benefits such as high nutritional value, low environmental impact, and versatility in various food applications make it an attractive option for vegans, vegetarians, and individuals looking to reduce their meat consumption. With ongoing research and development, vegan mycoprotein has the potential to revolutionize the food industry by providing a viable alternative to conventional animal-based proteins without compromising taste or nutrition. As we continue to prioritize health and sustainability, incorporating vegan mycoprotein into our diets can contribute to a more ethical and environmentally friendly food system.

