Mycoprotein Fungus, also known as Quorn, is a unique and innovative food source that has been gaining popularity in recent years. Derived from a filamentous fungus called Fusarium venenatum, mycoprotein offers a high-quality, sustainable protein alternative for those seeking to reduce their meat consumption or adopt a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle. With its meat-like texture, versatility in cooking, and impressive nutritional profile, Fungus has become a go-to ingredient for individuals looking to add more plant-based options to their diet without compromising on taste or texture. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, benefits, and potential uses of Fungus, shedding light on why it is considered a game-changer in the world of alternative proteins.

What is Fungus?
Fungus refers to a type of edible filamentous fungi that is commonly used in the production of vegetarian and vegan meat substitutes. The fungus, specifically known as Fusarium venenatum, is grown under controlled conditions using a fermentation process. It is rich in protein, low in fat, and contains essential amino acids, making it a popular alternative protein source for individuals who follow plant-based diets. Fungus is typically used to create textured meat-like products such as sausages, burgers, and nuggets, providing a sustainable and environmentally friendly option for those seeking meat alternatives.

How is Fungus produced?
Mycoprotein is produced using a fermentation process involving the Fusarium venenatum fungus. The fungus is cultivated in large fermenters, where it is fed with a nutrient-rich medium containing glucose and other essential minerals. Under controlled conditions of temperature and pH, the fungus grows and forms thread-like structures called mycelium. The mycelium is then harvested, heated, and undergoes a series of processing steps to remove excess moisture and enhance its texture and taste. Finally, the mycoprotein is used as an ingredient in various food products, such as meat substitutes or protein-rich vegetarian options.
What are the nutritional benefits and drawbacks of consuming Fungus?
Fungus, such as Quorn, offers several nutritional benefits. It is a rich source of complete protein, containing all essential amino acids required by the body. It is also low in saturated fat and cholesterol, making it a suitable option for individuals looking to reduce their intake of these nutrients. Additionally, Fungus is a good source of fiber, which aids in digestion and promotes satiety. However, there are some drawbacks to consider. Some people may be allergic to mycoprotein, experiencing symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Moreover, certain mycoprotein products may contain added ingredients that can be high in sodium or other less desirable nutrients. As with any food, moderation and reading labels are key to enjoying the benefits of mycoprotein while minimizing potential drawbacks.
Are there any potential health risks associated with consuming Fungus?
Consuming Mycoprotein Fungus, such as the one found in Quorn products, does not pose significant health risks for most individuals. However, there have been rare instances of allergic reactions to mycoprotein, which can manifest as gastrointestinal symptoms or skin rashes. Additionally, some studies suggest that excessive consumption of mycoprotein-based products may lead to a higher intake of certain minerals, such as zinc and copper, but these concerns are not well-established. It is always advisable to read product labels, consult a healthcare professional if allergic reactions occur, and maintain a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods.
What are the environmental impacts of cultivating Fungus?
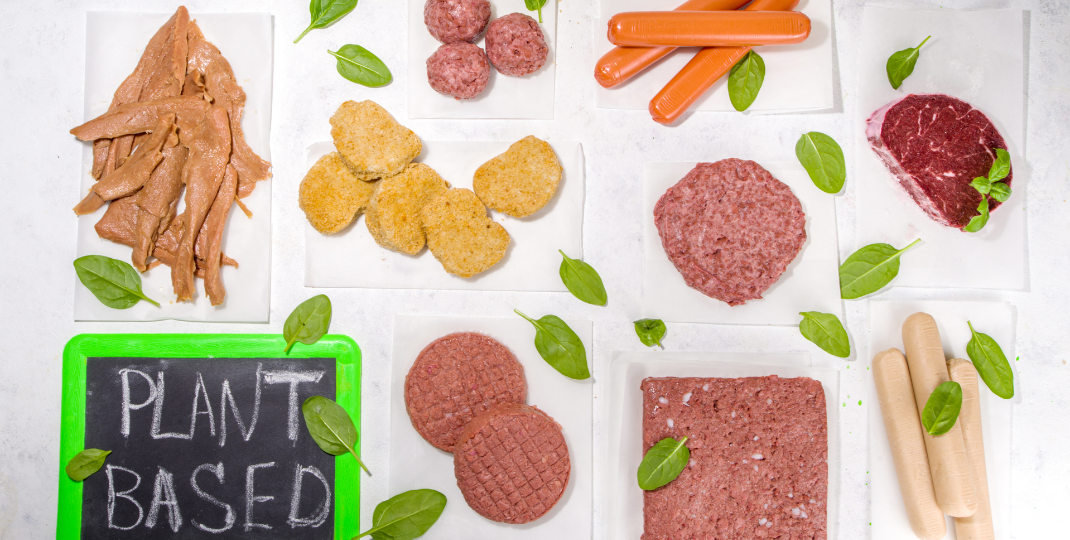

The cultivation of Fungus, commonly known as Quorn, has several environmental impacts. Firstly, it requires large amounts of energy and water to grow the fungus, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and putting pressure on water resources. Additionally, the cultivation process may involve the use of agricultural inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides, which can have negative effects on soil and water quality if not managed properly. Furthermore, the land required for growing the fungus could lead to deforestation or habitat destruction if not done sustainably. Therefore, while mycoprotein offers a plant-based protein alternative to meat, its cultivation should be carefully managed to minimize its environmental footprint.

How does Fungus compare to other protein sources in terms of taste and texture?
Fungus, also known as Quorn, has a unique taste and texture that differentiates it from other protein sources. It is often described as having a meat-like flavor with a slightly earthy or nutty undertone. In terms of texture, mycoprotein has a fibrous and chewy consistency, which is similar to some meat products. Unlike animal-based proteins, mycoprotein does not have the same juiciness or succulence but it can be prepared in various ways to enhance its taste and texture. Overall, mycoprotein offers a distinct sensory experience that may appeal to those seeking alternatives to traditional protein sources.
Are there any notable culinary uses or recipes that feature Fungus?
One notable culinary use of Fungus is its incorporation in vegetarian and vegan products as a meat substitute. Mycoprotein, often derived from a specific strain of filamentous fungus called Fusarium venenatum, has a unique fibrous texture that closely resembles meat. It can be used to make various meat alternatives, such as burgers, nuggets, sausages, and even meatballs. Additionally, mycoprotein can be flavored and seasoned differently to mimic the taste of different meats, allowing for a versatile range of dishes. Its high protein content and low fat content also make it a popular choice among those seeking a healthier alternative to meat.

What ongoing research or developments are happening in the field of Fungus?
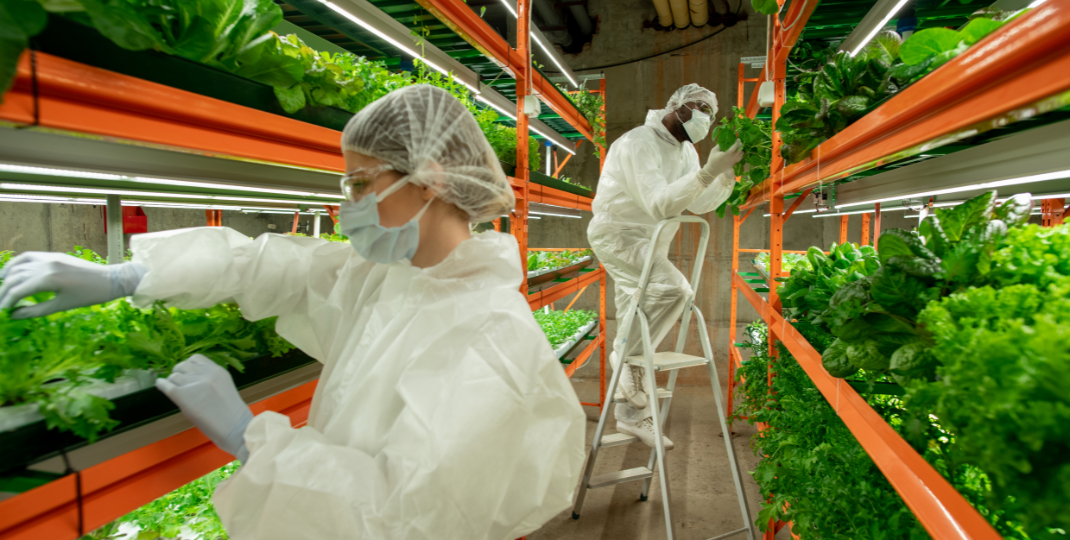

Ongoing research and developments in the field of Fungus aim to improve its production efficiency, nutritional content, and potential applications. Scientists are exploring various fermentation techniques, such as submerged and solid-state fermentation, to optimize the growth and biomass yield of mycoprotein fungi. Additionally, there is a focus on selecting and genetically modifying strains with desirable characteristics, such as high protein content or improved taste and texture. Furthermore, researchers are investigating the potential application of mycoprotein fungi in alternative protein sources, functional foods, animal feed, and biofuel production. Overall, the continuous advancements in understanding and harnessing the potential of Fungus offer promising prospects for sustainable and versatile applications in the food and biotechnology industries.
The Potential of Fungus in Food Production and Nutrition
In conclusion, Fungus is an innovative and sustainable source of protein that holds great potential for improving our food systems and addressing global challenges such as climate change and food security. Its unique characteristics, including its high protein content, low environmental impact, and versatility in various culinary applications, make it a promising alternative to traditional protein sources. With continued research and development, Fungus has the capacity to revolutionize the way we produce and consume protein, offering a more sustainable and nutritious future for individuals and the planet as a whole.