FBS cultured meat, also known as lab-grown meat or cell-based meat, is a groundbreaking innovation in the field of food production. Unlike conventionally farmed meat, which requires the raising and slaughtering of animals, FBS cultured meat is produced by harvesting animal cells and growing them in a laboratory-controlled environment. This technological advancement has the potential to revolutionize the way we obtain meat, offering a more sustainable and ethical alternative to traditional livestock farming. By eliminating the need for extensive land use, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and minimizing animal welfare concerns, FBS cultured meat represents a promising solution to address the challenges of global food security and environmental sustainability.

What is the current status of FBS cultured meat production?
Currently, the production of FBS (fetal bovine serum)-free cultured meat is still in the early stages of development. FBS, derived from unborn calves, is commonly used as a growth supplement in the cell culture media for cultivated meat production. However, due to ethical and sustainability concerns associated with its sourcing, efforts are underway to replace FBS with alternative growth fbs cultured meat factors and serum-free media formulations. Several companies and research institutions are actively working on developing FBS-free production methods, such as using plant-based or synthetic alternatives, or optimizing cell lines to reduce dependency on FBS. While progress has been made, substantial scale-up and commercialization of FBS-free cultured meat production is yet to be achieved.

How does FBS cultured meat differ in taste and texture compared to traditional meat?
FBS (Fetal Bovine Serum) cultured meat, also known as lab-grown or cell-based meat, is produced by culturing animal cells in a laboratory instead of raising and slaughtering animals. In terms of taste and texture, FBS cultured meat aims to closely replicate the qualities of traditional meat. The cells used in the process are derived from real animals, and scientists work to optimize the growth conditions to ensure similar muscle tissue characteristics. While the exact taste and texture may vary depending on the specific production methods, studies have shown that FBS cultured meat can closely resemble traditional meat, offering a similar eating experience while reducing the environmental impact associated with conventional meat production.
Are there any ethical concerns associated with FBS cultured meat production?
There are several ethical concerns associated with FBS (fetal bovine serum) cultured meat production. Firstly, the use of FBS involves the slaughter of pregnant cows to obtain the serum from their fetuses, raising ethical concerns about animal welfare and unnecessary harm. Additionally, the demand for FBS in cultured meat production could lead to an increase in the number of cows being bred solely for this purpose, which raises questions about the ethics of using animals as mere commodities for human consumption. Furthermore, there is a need to consider the long-term sustainability and environmental impact of large-scale FBS production, as it can have significant resource requirements and contribute to climate change. Overall, the ethical concerns surrounding FBS cultured meat production highlight the importance of developing alternative methods or sourcing options that prioritize animal welfare, sustainability, and respect for all living beings involved.
What are the long-term environmental impacts of scaling up FBS cultured meat production?
Scaling up FBS (fetal bovine serum) cultured meat production has several long-term environmental impacts. Firstly, the production of FBS requires the extraction of blood from pregnant cows, which can lead to ethical concerns and animal welfare issues. Secondly, the increasing demand for FBS may result in more significant pressure on the global cattle industry, leading to deforestation, habitat destruction, and increased greenhouse gas emissions associated with cattle farming. Additionally, the large-scale production of FBS cultured meat would require substantial amounts of energy, water, and land, further contributing to resource depletion and potential pollution. Therefore, while cultured meat offers a promising solution to reduce the environmental impact of traditional livestock farming, it is crucial to develop sustainable alternatives to FBS to ensure that the overall environmental benefits are realized.
How affordable is FBS cultured meat compared to conventional meat?
FBS (fetal bovine serum) cultured meat, also known as lab-grown or cell-based meat, is currently more expensive compared to conventional meat. This is primarily due to the high cost of FBS, which is used as a growth medium in the production process. FBS is derived from the blood of unborn calves and its limited availability and ethical concerns have driven fbs cultured meat up its price. However, advancements in research and development are being made to find alternative, more affordable growth mediums that can replace FBS in the future. As technology improves and economies of scale kick in, it is expected that the cost of cultured meat will decrease, making it more accessible and competitive with conventional meat.

What regulatory challenges exist for FBS cultured meat and how are they being addressed?
There are several regulatory challenges that exist for FBS (fetal bovine serum) cultured meat. FBS is commonly used as a growth medium in the production of cultured meat, but its use raises concerns regarding animal welfare, sustainability, and potential health risks. To address these challenges, regulators are working on developing alternative growth media that do not rely on FBS. They are also exploring ways to ensure the safety and quality of cultured meat products through rigorous testing and inspection procedures. Additionally, there is a need for clear labeling and transparency to inform consumers about the nature and production methods of cultured meat. Collaboration between industry stakeholders, scientists, and regulatory bodies is essential to establish comprehensive guidelines and regulations that promote the responsible and sustainable development of FBS cultured meat.
Are there any health risks or benefits associated with consuming FBS cultured meat?
There are both potential health risks and benefits associated with consuming FBS (fetal bovine serum) cultured meat. On the one hand, as FBS is derived from fetal calves, there may be concerns related to animal welfare and ethical considerations. Additionally, FBS can contain hormones, growth factors, and other components that might raise concerns about the potential transmission of diseases or allergies. On the other hand, FBS cultured meat has the potential to reduce the environmental impact of conventional meat production, decrease the use of antibiotics, and potentially provide a more controlled and safer food source. However, further research and regulation are necessary to fully understand and address any potential health risks or benefits associated with consuming FBS cultured meat.

How does FBS cultured meat contribute to food security and sustainable agriculture?
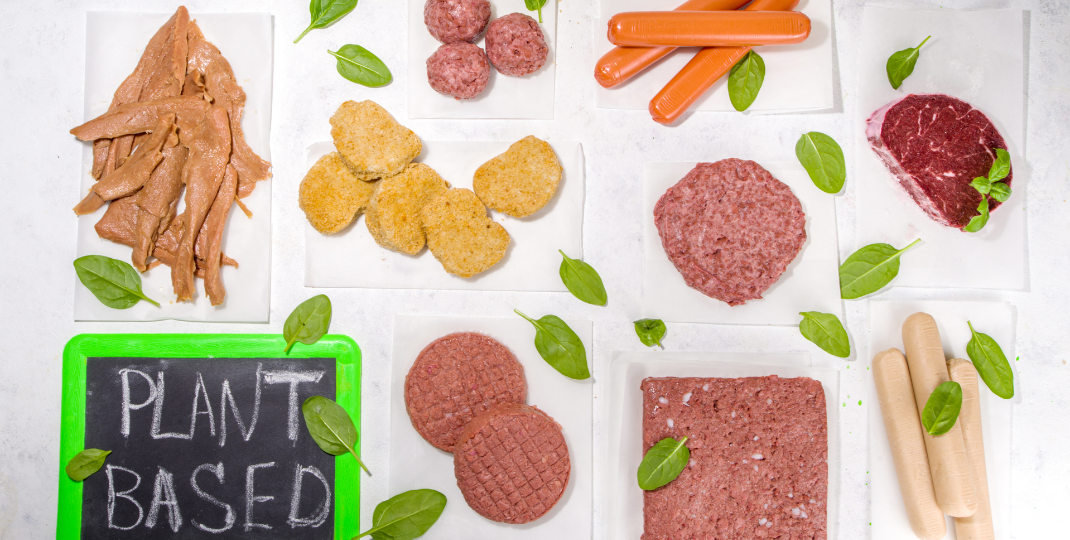

FBS cultured meat, also known as lab-grown or cell-based meat, contributes to food security and sustainable agriculture in multiple ways. Firstly, it reduces the reliance on traditional livestock farming, which is resource-intensive, requires vast amounts of land, and contributes to deforestation and greenhouse gas emissions. Cultured meat production can be done in controlled environments with minimal land use and lower environmental impact. Secondly, it provides a solution to the increasing global demand for protein-rich food by producing meat without the need for animal slaughter. This technology has the potential to address food shortages, especially in regions where traditional meat production is limited. Overall, FBS cultured meat offers a more sustainable and efficient method of meat production, contributing to long-term food security and reducing the ecological footprint of agriculture.
FBS Cultured Meat: Revolutionizing the Future of Food Production
In conclusion, FBS cultured meat holds great promise for the future of sustainable food production. With its ability to replicate the taste and texture of conventional meat while eliminating the need for traditional livestock farming, it addresses pressing challenges such as environmental degradation, animal welfare concerns, and food security. Although further research and development are needed to improve scalability and reduce production costs, FBS cultured meat has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce and consume meat, paving the way for a more ethical and environmentally-friendly food system.
