Extraction of enzymes from plants is a crucial process in the field of biotechnology and pharmaceuticals. Enzymes are essential biological molecules that catalyze various biochemical reactions, making them invaluable in industries ranging from food and beverage production to medicine. Plants serve as a rich source of enzymes, with each species containing a unique set of these catalysts with diverse functions. By extracting enzymes from plants, researchers can harness their potential for developing innovative products and therapies that could benefit society in numerous ways. This extraction process involves meticulous techniques to isolate and purify the enzymes effectively, ensuring their optimal functionality and stability for use in various applications. Through advancements in extraction methods and technology, scientists continue to explore the vast potential of plant-derived enzymes for enhancing various industrial processes and improving human health.
Methods for Extracting Enzymes from Plants
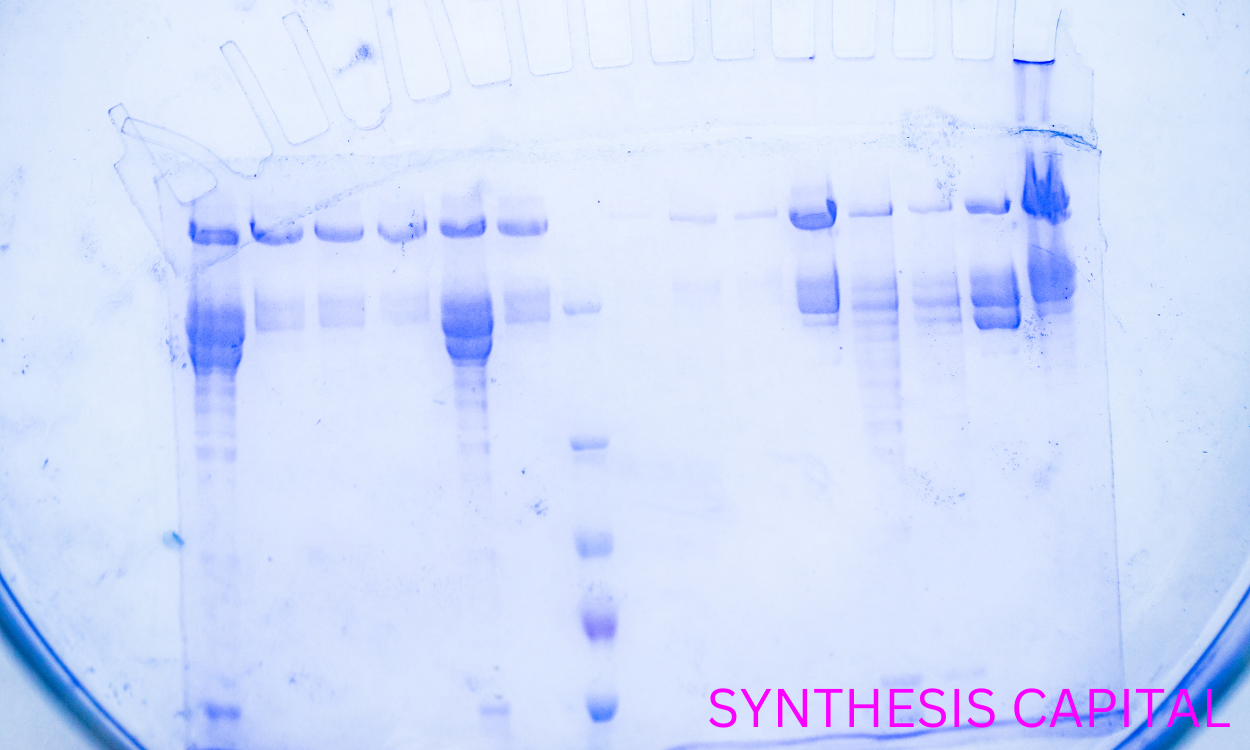
Enzymes can be extracted from plants using various methods such as maceration, homogenization, and filtration. In maceration, the plant material is soaked in a solvent to soften it and release enzymes, which are then separated through filtration or centrifugation. Homogenization involves breaking down the plant cells to release enzymes by grinding or blending the material. Filtration is often used to separate the enzyme-containing liquid from solid plant material. Additionally, some enzymes can be extracted using techniques like ultrasonication or supercritical fluid extraction, which utilize sound waves or high-pressure fluids to disrupt plant cells and release enzymes more efficiently. These methods allow for the extraction of enzymes from plants in a cost-effective and environmentally friendly manner.

How do different plant species differ in the types and quantities of enzymes they produce?
Different plant species differ in the types and quantities of enzymes they produce due to variations in their genetic makeup and environmental factors. Enzymes are crucial for plant growth and development, as they catalyze various biochemical reactions within the cells. Plants have evolved to produce specific enzymes that are tailored to their needs based on factors such as nutrient availability, temperature, and light intensity. These differences in enzyme production contribute to the diverse characteristics observed among plant species, including their growth patterns, adaptations to different environments, and metabolic functions. Additionally, some plant species may produce unique enzymes that are not found in other species, further contributing to their distinct biochemical profiles.
Are there any risks or limitations associated with extracting enzymes from plants?
There are potential risks and limitations associated with extracting enzymes from plants, such as variability in enzyme concentration depending on plant species, the need for large quantities of plant material to obtain sufficient enzyme yields, and the possibility of contamination or impurities in the extracted enzymes that could affect their effectiveness. Additionally, there may be challenges in scaling up production and ensuring consistent quality and purity of the enzymes extracted from plants. Furthermore, some plant species may contain toxic compounds or allergens that could pose a risk if not properly removed during the extraction process.
How can the purity and efficiency of enzyme extraction from plants be optimized?
The purity and efficiency of enzyme extraction from plants can be optimized by carefully selecting the plant source with high enzyme content, using appropriate extraction methods such as grinding or blending the plant material to release enzymes effectively, optimizing extraction buffers and conditions to maintain enzyme stability, utilizing purification techniques like filtration or chromatography to remove impurities, and monitoring enzyme activity throughout the extraction process to ensure high quality and yield of enzymes. Additionally, conducting thorough research on the specific enzymes of interest and their optimal extraction conditions can further enhance the purity and efficiency of enzyme extraction from plants.
What are the potential applications of plant-derived enzymes in various industries?
Plant-derived enzymes have a wide range of potential applications in various industries due to their ability to catalyze biochemical reactions efficiently and sustainably. In the food industry, these enzymes can be used for processes such as brewing, baking, and cheese production, improving product quality and reducing processing time. In the textile industry, plant-derived enzymes are utilized for fabric finishing and bio-polishing, leading to softer, more durable textiles with minimal environmental impact. Furthermore, in the pharmaceutical industry, these enzymes play a crucial role in drug synthesis and formulation, offering safer and more cost-effective alternatives to chemical catalysts. Overall, the versatility and eco-friendly nature of plant-derived enzymes make them valuable tools in enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of various industrial processes.
Impact of Environmental Factors on Enzyme Production in Plants
Environmental factors such as soil composition and climate play a crucial role in influencing enzyme production in plants. Soil composition affects the availability of essential nutrients and minerals required for enzymatic activity, with deficiencies leading to decreased enzyme production. Additionally, pH levels in the soil can impact the functioning of enzymes. Climate factors like temperature and moisture levels also influence enzyme production by affecting plant metabolism, protein synthesis, and overall growth. Extreme conditions can disrupt enzyme function and limit the plant's ability to produce enzymes necessary for various biochemical processes essential for growth and development. Overall, environmental factors significantly impact enzyme production in plants and ultimately determine their ability to thrive in their specific surroundings.
Exploring Ethical Considerations in Plant Enzyme Extraction
When extracting enzymes from plants, ethical considerations to take into account may include ensuring that the extraction process does not harm the overall health and well-being of the plant, as well as considering the sustainability of the plant species being used. It is important to conduct the extraction in a way that does not deplete or endanger the plant population, and to potentially explore alternative methods that are more environmentally friendly. Additionally, there may be ethical concerns related to the labor practices involved in harvesting and processing the plants for enzyme extraction, such as ensuring fair wages and working conditions for those involved in the process. Overall, it is crucial to approach the extraction of enzymes from plants with a mindful and ethical perspective to ensure that it is done in a responsible and sustainable manner.
What advancements have been made in the field extraction of enzymes from plants of plant enzyme extraction in recent years?
Recent advancements in plant enzyme extraction have focused on improving efficiency, yield, and specificity of the enzymes extracted. Innovations such as the use of novel extraction methods like ultrasound-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, and enzyme-assisted extraction have been developed to enhance the extraction process. Additionally, the development of new enzyme purification techniques, such as membrane technology and chromatography, have enabled researchers to isolate and purify plant enzymes more effectively. Furthermore, advances in biotechnology have allowed for the engineering of plants to produce higher levels of specific enzymes, leading to increased production capabilities. Overall, these advancements have paved the way for the commercialization of plant enzymes for various industrial applications, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, and biofuel production.
The Efficiency of Plant Enzyme Extraction Methods
1. Select the appropriate plant material for enzyme extraction based on the desired enzyme activity.

2. Use gentle extraction methods to preserve enzyme extraction of enzymes from plants activity, such as cold pressing or maceration.
3. Consider using organic solvents or buffer solutions to aid in enzyme extraction.
4. Monitor extraction conditions carefully to prevent denaturation of enzymes.