The Cultivated Meat industry, also known as lab-grown or cell-based meat, is a groundbreaking field that revolutionizes the way we produce and consume meat. This emerging industry aims to create real meat products without the need for traditional animal agriculture, making it a more sustainable and ethical alternative. By cultivating cells in a lab setting, scientists and researchers are able to grow meat that is identical to conventional animal meat, but with reduced environmental impact and without the need for animal slaughter. With the potential to address some of the most pressing challenges facing our food system, the Meat industry is poised to transform the way we think about meat production and consumption.

What are the long-term environmental impacts of the Meat industry?
The long-term environmental impacts of the Meat industry can be positive compared to traditional livestock farming methods. Cultivated meat, also known as lab-grown or cell-based meat, is produced from animal cells without the need for raising and slaughtering animals. This significantly reduces land use, water consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions associated with livestock farming. Additionally, it minimizes the use of antibiotics and decreases the risk of zoonotic diseases. However, there are still challenges in terms of energy usage, waste management, and scaling up production that need to be addressed to fully assess and mitigate the environmental impacts of the Meat industry.
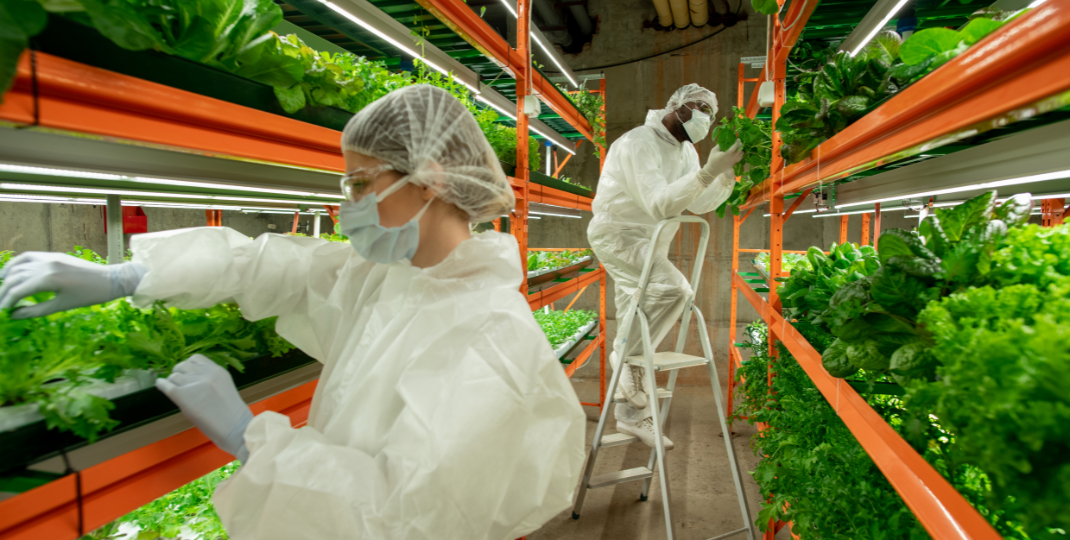

How will the taste and texture of cultivated meat compare to traditional animal-based meat?
The taste and texture of cultivated meat are expected to be very similar to traditional animal-based meat. Through tissue engineering techniques, scientists can replicate the cells and structure of animal muscle, resulting in a product that closely resembles conventional meat in terms of flavor and mouthfeel. The composition and nutritional value of cultivated meat can also be controlled, making it possible to create healthier and more sustainable alternatives without compromising on taste and texture.
What are the potential social implications of a widespread shift to cultivated meat production?
A widespread shift to cultivated meat production could have several potential social implications. Firstly, it may lead to a reduction in the demand for traditional livestock farming, which could impact the livelihoods of farmers and workers in the agricultural sector. Additionally, the shift could result in a change in dietary patterns and cultural practices associated with meat consumption, potentially causing resistance or acceptance from different communities and regions. Furthermore, there may be concerns regarding the environmental sustainability of large-scale cellular agriculture and its long-term effects on ecosystems. The acceptance and adoption of cultivated meat could also raise ethical debates and challenges related to animal welfare, genetic modification, and ownership of intellectual property rights. It is important to consider these implications and engage in discussions to ensure a balanced and inclusive transition towards cultivated meat production.
How will the cost of cultivated meat compare to conventional meat in the future?
In the future, it is expected that the cost of cultivated meat will decrease and eventually become competitive with conventional meat. Currently, the production process for cultivated meat is expensive, mainly due to the high costs of cell culture media and growth factors. However, as technology advances and economies of scale are achieved, the cost of production is projected to decline significantly. Additionally, improvements in cell culture techniques and efficiency will further contribute to cost reduction. With these developments, it is anticipated that cultivated meat will eventually be available at similar or lower prices than conventional meat, making it a more viable and sustainable alternative.
What are the potential health effects of consuming cultivated meat on a regular basis?
Consuming cultivated meat on a regular basis has the potential to have several positive health effects. Firstly, it can provide a sustainable and ethical alternative to traditional meat production, reducing the environmental impact and animal welfare concerns associated with conventional meat consumption. Secondly, cultivated meat has the potential to be free from harmful pathogens and antibiotic residues commonly found in conventionally produced meat. Additionally, as cultivated meat is produced in a controlled environment, it can be designed to have lower levels of saturated fat and higher levels of beneficial nutrients, making it a healthier option compared to traditional meat. However, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term health effects of consuming cultivated meat and ensure its safety and nutritional value.

How will the global food system be transformed if cultivated meat becomes the norm?
If cultivated meat becomes the norm, it has the potential to transform the global food system in several ways. Firstly, it could significantly reduce the environmental impact of traditional livestock farming, such as deforestation and greenhouse gas emissions, as cultivated meat production requires fewer resources and produces fewer waste products. Additionally, it could address the ethical concerns surrounding animal welfare by eliminating the need for raising and slaughtering animals. Furthermore, cultivated meat has the potential to enhance food security by reducing the reliance on traditional farming methods that are susceptible to unpredictable weather conditions and disease outbreaks. Overall, the widespread adoption of cultivated meat could lead to a more sustainable, ethical, and secure global food system.
What are the challenges and limitations of scaling up cultivated meat production to meet global demand?
Scaling up cultivated meat production to meet global demand faces several challenges and limitations. Firstly, the high cost of production is a significant hurdle. Cultivated meat is currently expensive due to the need for expensive growth media and bioreactors, making it inaccessible for mass consumption. Additionally, scaling up production requires a reliable and scalable source of animal cells, which may be challenging to obtain at a large scale. Another limitation is the difficulty in replicating the complex texture and taste of traditional meat. Efforts are underway to overcome this hurdle, but achieving the same sensory experience as conventional meat remains a challenge. Regulatory approval and public acceptance are also potential obstacles that could slow down the scaling process. However, addressing these challenges through technological advancements, cost reduction, and consumer education can pave the way for a more sustainable and cruelty-free meat industry.

How will the regulatory landscape evolve to accommodate the growing ?

The regulatory landscape is expected to evolve in order to accommodate the growing Cultivated Meat industry. As this emerging technology advances, regulators will likely establish a clear set of guidelines and standards to ensure the safety and quality of cultivated meat products. This may involve creating specific regulations for cell-based meat production facilities, labeling requirements, and oversight of the entire supply chain. Additionally, collaborations between industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies will be crucial in addressing any potential concerns and developing a framework that promotes consumer trust and confidence in cultivated meat. Overall, the regulatory landscape will adapt to support the growth and development of this innovative industry while ensuring the protection of public health and environmental sustainability.
The Rise of Meat industry: Revolutionizing the Future of Food
In conclusion, the Meat industry holds immense potential to revolutionize the way we produce meat and address the numerous challenges associated with traditional animal agriculture. With its ability to eliminate the need for animal slaughter, reduce environmental impact, and offer a more sustainable and ethical alternative, cultivated meat has garnered significant attention and investment from both scientists and entrepreneurs worldwide. While there are still technical and regulatory hurdles to overcome, the continuous advancements in cellular agriculture and growing consumer demand for sustainable food options make it clear that the Meat industry is poised for tremendous growth and could be a game-changer in the global food system.
